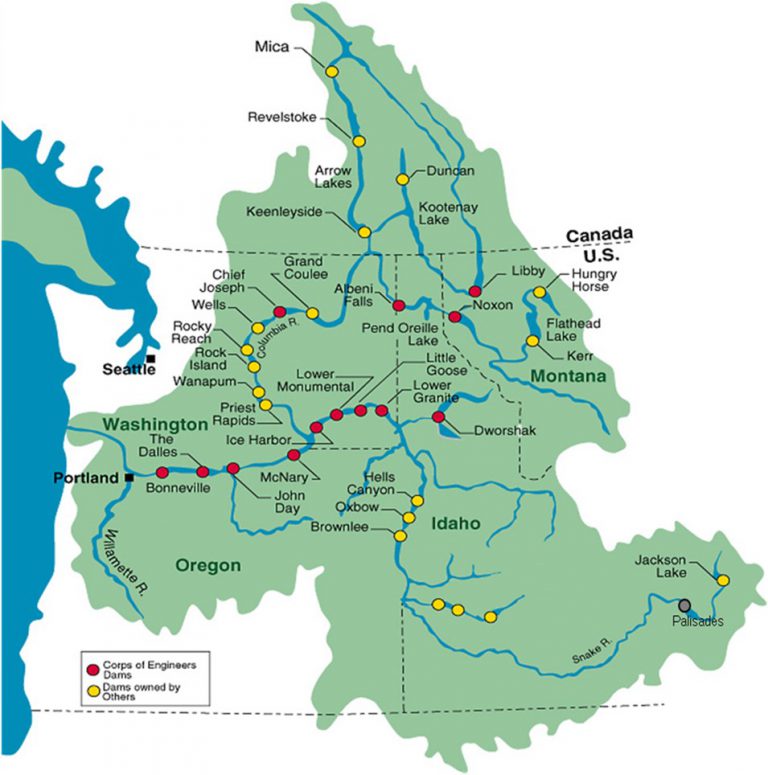
The Columbia River, one of the most significant rivers in North America, plays a crucial role in the economic, environmental, and social landscapes of both the United States and Canada. As the river traverses international borders, it brings forth a series of challenges and opportunities that require collaborative efforts between the two nations. This article delves into the complexities surrounding the Columbia River, examining its historical significance, current challenges, and potential solutions.
As a vital waterway, the Columbia River has been a focal point for discussions regarding resource management, treaty agreements, and environmental sustainability. The river's importance extends beyond its role as a natural resource; it serves as a lifeline for communities, industries, and ecosystems on both sides of the border. Understanding the challenges faced by the Columbia River is essential for ensuring its sustainable future.
This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the U.S.-Canada challenges arising from the Columbia River's management. By exploring the historical context, legal frameworks, environmental concerns, and socio-economic implications, we aim to shed light on the complexities of this transboundary issue. Let us embark on this journey to uncover the intricacies of the Columbia River's role in shaping the relationship between the United States and Canada.
Read also:Does Walmart Accept Amex A Comprehensive Guide For Smart Shoppers
Table of Contents:
- History of the Columbia River
- Columbia River Treaty: A Historical Perspective
- Key Challenges of the Columbia River
- Environmental Concerns and Conservation Efforts
- Economic Impacts and Opportunities
- Indigenous Perspectives and Rights
- Legal Frameworks and Policy Developments
- Future Prospects and Collaborative Solutions
- Technological Innovations in River Management
- Conclusion and Call to Action
History of the Columbia River
The Columbia River, originating in British Columbia, Canada, and flowing into the Pacific Ocean in the United States, has a rich history that dates back thousands of years. Indigenous peoples have relied on the river for sustenance, transportation, and cultural significance. The river's discovery by European explorers in the late 18th century marked the beginning of a new era, characterized by colonization, industrialization, and resource exploitation.
Early Exploration and Settlement
The first recorded exploration of the Columbia River occurred in 1792 when Captain Robert Gray, an American trader, sailed into the river's mouth. This discovery paved the way for further exploration and settlement, leading to the establishment of fur trading posts and the eventual colonization of the region. The river became a vital artery for trade and transportation, connecting inland communities to the coast.
Industrialization and Development
During the 19th and 20th centuries, the Columbia River underwent significant industrialization. Dams were constructed along its course to harness hydroelectric power, support irrigation, and facilitate navigation. While these developments brought economic benefits, they also introduced environmental and social challenges that persist to this day.
Columbia River Treaty: A Historical Perspective
The Columbia River Treaty, signed in 1964, is a landmark agreement between the United States and Canada aimed at coordinating the management of the river's water resources. The treaty focuses on flood control and hydropower generation, with both nations sharing the benefits and responsibilities of dam construction and operation.
Key Provisions of the Treaty
- Construction of dams in Canada to regulate water flow and prevent flooding in downstream areas.
- Shared revenue from hydropower generation, ensuring equitable economic benefits for both countries.
- Collaborative decision-making processes to address emerging challenges and opportunities.
While the treaty has been successful in achieving its primary objectives, it has also faced criticism for its limited focus on environmental and indigenous concerns. As the treaty approaches its review period, discussions are underway to address these gaps and modernize its provisions.
Read also:Discover The Best Of Downtown San Ramon Hotels
Key Challenges of the Columbia River
The Columbia River faces a multitude of challenges that require urgent attention and collaborative action. These challenges encompass environmental, socio-economic, and political dimensions, affecting the river's health and the communities that depend on it.
Environmental Degradation
One of the most pressing challenges is the degradation of the river's ecosystem. Dams, pollution, and climate change have disrupted natural water flows, affecting fish populations, habitats, and water quality. Restoring the river's ecological balance is a priority for both nations.
Socio-Economic Impacts
The Columbia River supports a wide range of industries, including agriculture, fishing, and tourism. However, changes in water availability and quality can have adverse effects on these sectors, impacting livelihoods and regional economies. Addressing these impacts requires comprehensive planning and stakeholder engagement.
Environmental Concerns and Conservation Efforts
Protecting the Columbia River's environment is critical for ensuring its long-term sustainability. Efforts are underway to address key environmental concerns and implement conservation measures that benefit both nature and people.
Restoration of Fish Populations
Salmon and other fish species are integral to the Columbia River's ecosystem and cultural heritage. Restoration programs aim to enhance fish passage, improve habitat conditions, and mitigate the impacts of dams and other barriers. Collaborative initiatives between governments, indigenous communities, and conservation organizations are essential for the success of these programs.
Water Quality Management
Maintaining water quality is a priority for the health of the river and its users. Pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, and urban development poses significant risks to water quality. Implementing effective wastewater treatment systems and promoting sustainable practices can help mitigate these risks.
Economic Impacts and Opportunities
The Columbia River contributes significantly to the economies of the United States and Canada. Its resources support diverse industries, offering opportunities for growth and innovation. However, balancing economic development with environmental protection remains a challenge.
Hydropower Generation
Hydropower is a major source of renewable energy in the Columbia River Basin. The region's dams generate electricity that powers millions of homes and businesses. Enhancing the efficiency of hydropower systems and integrating them with other renewable energy sources can further reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainability.
Agricultural Irrigation
The river's water supports extensive agricultural activities, providing irrigation for crops such as wheat, fruits, and vegetables. Ensuring sustainable water management practices is essential for maintaining agricultural productivity while minimizing environmental impacts.
Indigenous Perspectives and Rights
Indigenous communities have deep historical and cultural connections to the Columbia River. Their perspectives and rights must be respected and integrated into decision-making processes related to the river's management.
Recognition of Indigenous Sovereignty
Indigenous nations along the Columbia River have advocated for greater recognition of their sovereignty and involvement in resource management. Collaborative agreements and partnerships can help ensure that indigenous voices are heard and their rights are upheld.
Cultural Heritage Preservation
Preserving the cultural heritage of indigenous communities is crucial for maintaining the river's cultural significance. Initiatives to protect sacred sites, traditional knowledge, and cultural practices can contribute to a more inclusive and respectful approach to river management.
Legal Frameworks and Policy Developments
Effective legal frameworks and policies are essential for addressing the challenges faced by the Columbia River. These frameworks must be adaptable to changing circumstances and inclusive of diverse stakeholders.
Modernizing the Columbia River Treaty
Ongoing discussions aim to modernize the Columbia River Treaty to better address contemporary challenges, such as climate change, environmental protection, and indigenous rights. Ensuring that the treaty reflects current priorities and values is vital for its continued relevance and effectiveness.
National and International Cooperation
Cooperation between national governments, regional authorities, and international organizations is critical for achieving sustainable river management. Sharing best practices, resources, and knowledge can enhance the effectiveness of collaborative efforts.
Future Prospects and Collaborative Solutions
Looking ahead, the future of the Columbia River depends on the willingness of stakeholders to work together towards common goals. By embracing innovative solutions and fostering collaboration, the river's challenges can be transformed into opportunities for positive change.
Adapting to Climate Change
Climate change poses significant risks to the Columbia River's water resources, ecosystems, and communities. Developing adaptive strategies and resilience measures is essential for mitigating these risks and ensuring the river's sustainability.
Encouraging Public Participation
Involving the public in river management decisions can enhance transparency, accountability, and innovation. Public education campaigns, participatory planning processes, and community engagement initiatives can help build a shared vision for the river's future.
Technological Innovations in River Management
Technological advancements offer new possibilities for improving the management of the Columbia River. From data analytics to remote sensing, these innovations can enhance our understanding of the river's dynamics and inform evidence-based decision-making.
Monitoring and Data Collection
Advanced monitoring systems and data collection technologies can provide real-time information on water levels, flow rates, and water quality. This information is invaluable for managing the river's resources effectively and responding to emergencies promptly.
Smart Infrastructure Development
Investing in smart infrastructure, such as smart dams and water management systems, can optimize resource use and reduce environmental impacts. These technologies can also improve operational efficiency and reduce costs, benefiting both the environment and the economy.
Conclusion and Call to Action
The Columbia River's U.S.-Canada challenges arise from a complex interplay of environmental, socio-economic, and political factors. Addressing these challenges requires a commitment to collaboration, innovation, and sustainability. By working together, stakeholders can ensure that the river continues to provide benefits for future generations.
We invite you to join the conversation and take action to support the sustainable management of the Columbia River. Share your thoughts in the comments section, explore related articles on our website, and stay informed about developments in this critical area. Together, we can make a difference in shaping the future of this vital resource.