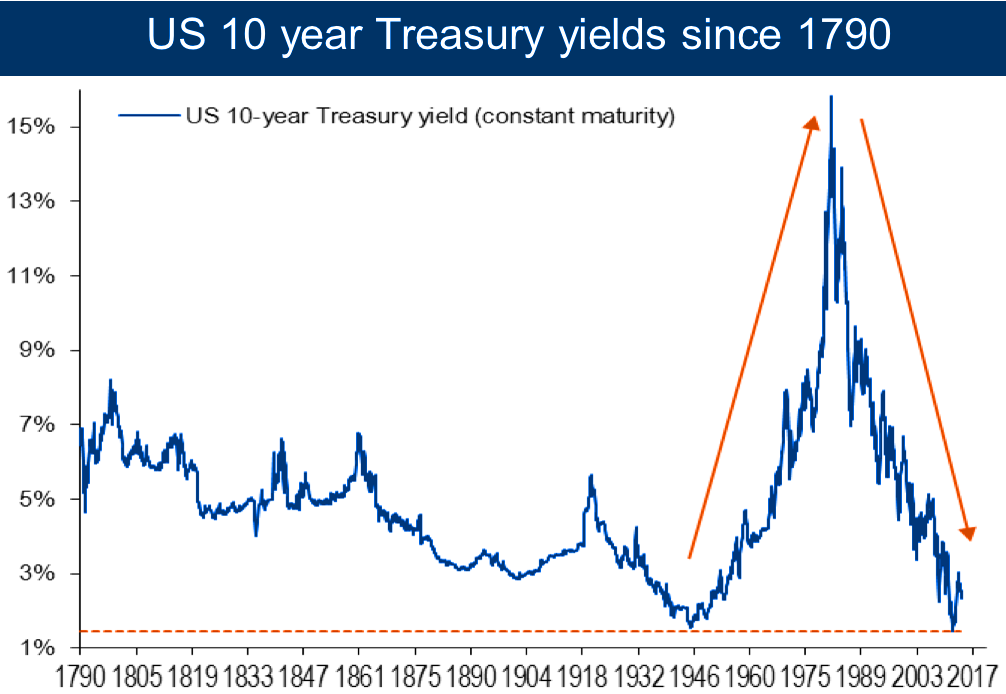
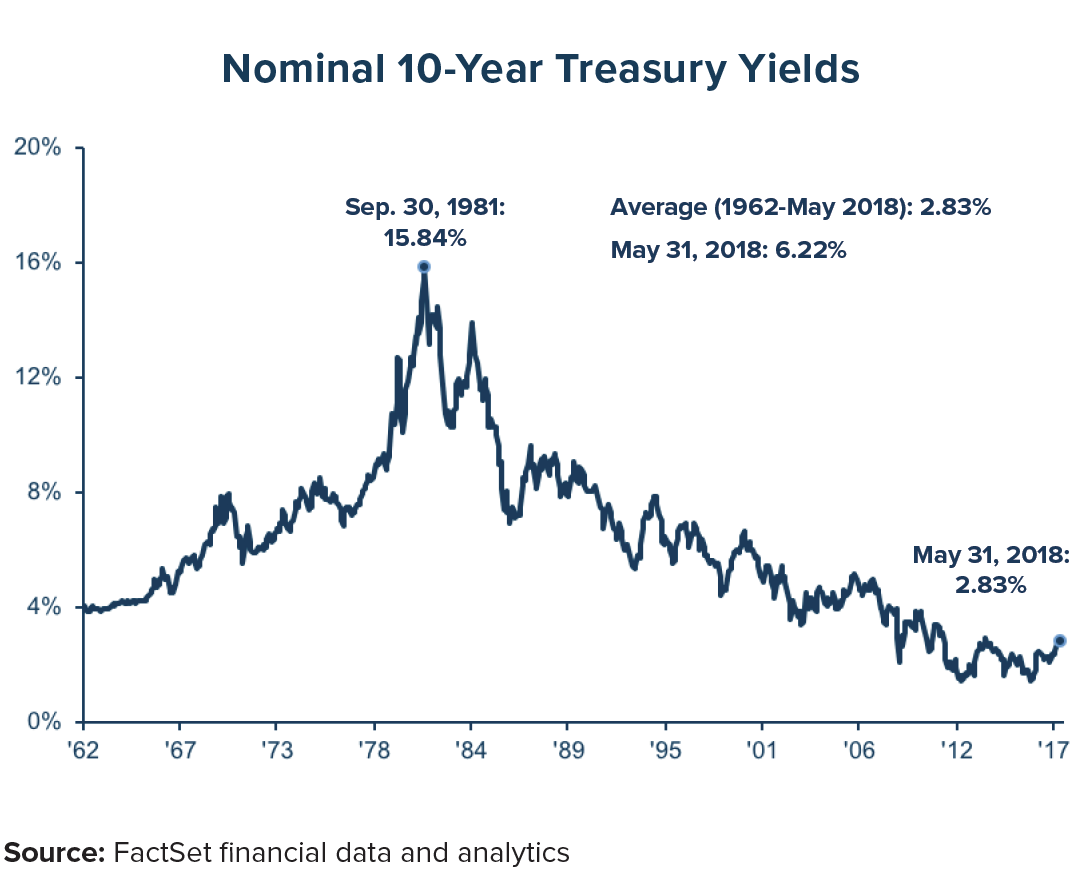
The 10-year treasury note has long been considered a critical benchmark in the financial world. It is a debt obligation issued by the U.S. government, offering investors a secure way to earn returns while supporting national economic growth. This instrument is not only a staple for investors but also a key indicator of economic health and market sentiment.
As one of the most widely followed fixed-income securities globally, the 10-year treasury plays a pivotal role in shaping monetary policy decisions and influencing interest rates across various sectors. Its yields serve as a benchmark for other financial products, such as mortgages, corporate bonds, and loans.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the 10-year treasury, its significance, and its impact on global markets. Whether you're an investor, economist, or simply curious about how this financial instrument works, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions.
Read also:Aaron Gordon The Rising Star In The Nba
Table of Contents
- Introduction to 10-Year Treasury
- A Brief History of Treasury Notes
- Structure of the 10-Year Treasury
- How the 10-Year Treasury Functions
- Impact on Global Markets
- Understanding the Yield Curve
- Investor Perspective on 10-Year Treasuries
- Risks Associated with 10-Year Treasury Investments
- Current Trends in the 10-Year Treasury Market
- Future Outlook for 10-Year Treasury Notes
- Conclusion
Introduction to 10-Year Treasury
The 10-year treasury note is a government bond with a maturity period of 10 years. It is issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury and is considered one of the safest investments globally due to the creditworthiness of the U.S. government. Investors purchase these notes to receive periodic interest payments and the return of principal upon maturity.
Why is the 10-Year Treasury Important?
The 10-year treasury serves as a benchmark for long-term interest rates, influencing mortgage rates, auto loans, and other financial products. Its yield is closely monitored by economists and investors as an indicator of market expectations regarding future economic conditions.
Who Buys 10-Year Treasury Notes?
- Institutional investors such as pension funds and insurance companies
- Central banks and sovereign wealth funds
- Individual investors seeking low-risk investments
A Brief History of Treasury Notes
Treasury notes have been a cornerstone of U.S. finance since the late 18th century. The first issuance of treasury securities occurred in 1790 to fund the Revolutionary War debt. Over time, the U.S. Treasury expanded its offerings to include various maturities, with the 10-year note becoming a staple in the mid-20th century.
Read also:Ralph Macchio The Iconic Actors Journey Through Hollywood
Key Milestones in Treasury Note History
- 1929: The introduction of long-term treasury bonds
- 1950s: Regular issuance of 10-year notes to stabilize post-war finances
- 2008: Increased demand during the financial crisis as investors sought safe havens
Today, the 10-year treasury remains a critical component of global financial markets, reflecting the enduring trust in U.S. fiscal policy.
Structure of the 10-Year Treasury
The 10-year treasury note is structured to provide investors with predictable returns. It is issued with a fixed interest rate, known as the coupon rate, and pays interest semi-annually. The face value, or par value, is returned to investors at maturity.
Key Features of the 10-Year Treasury
- Maturity: 10 years from issuance
- Coupon Rate: Fixed interest rate determined at auction
- Interest Payments: Paid semi-annually
- Face Value: Typically $1,000 per note
This structure ensures that investors receive consistent income while preserving capital, making it an attractive option for conservative portfolios.
How the 10-Year Treasury Functions
The 10-year treasury operates through a bidding process conducted by the U.S. Treasury Department. Investors submit competitive and non-competitive bids to purchase these securities at auctions held regularly throughout the year.
Auction Process
During auctions, the Treasury determines the coupon rate based on the highest bids received. Investors who submit competitive bids may receive a lower yield if their bids are below the cutoff rate. Non-competitive bidders, however, are guaranteed to receive the full amount of their purchase at the determined yield.
This auction mechanism ensures transparency and fairness in the allocation of treasury notes, fostering trust in the financial system.
Impact on Global Markets
The 10-year treasury's influence extends far beyond U.S. borders. Its yields affect global financial markets by setting benchmarks for interest rates worldwide. For instance, when the 10-year treasury yield rises, it often leads to higher borrowing costs for businesses and consumers globally.
How Does the 10-Year Treasury Affect Other Markets?
- Influences mortgage rates and housing markets
- Impacts corporate bond yields and borrowing costs
- Shapes currency exchange rates and trade balances
Investors worldwide closely monitor the 10-year treasury yield as a barometer of economic health and investor sentiment.
Understanding the Yield Curve
The yield curve, which plots the yields of treasury securities across different maturities, provides valuable insights into market expectations. The 10-year treasury plays a central role in this curve, often serving as the midpoint between short-term and long-term rates.
What Does the Yield Curve Tell Us?
- A normal yield curve indicates economic growth and stability
- An inverted yield curve may signal an impending recession
- A flat yield curve suggests uncertainty or transition in economic conditions
By analyzing the yield curve, economists and investors can anticipate potential shifts in monetary policy and economic trends.
Investor Perspective on 10-Year Treasuries
For investors, the 10-year treasury offers a unique combination of safety and return. While it may not offer the high yields of riskier assets, its stability and liquidity make it an essential component of diversified portfolios.
Advantages of Investing in 10-Year Treasuries
- Low default risk due to U.S. government backing
- Predictable income stream through fixed interest payments
- Liquidity, as these securities are actively traded in secondary markets
Despite its advantages, investors must weigh the trade-offs between safety and potential returns when considering 10-year treasury investments.
Risks Associated with 10-Year Treasury Investments
While the 10-year treasury is considered a safe investment, it is not entirely risk-free. Factors such as inflation, interest rate fluctuations, and geopolitical events can impact its value.
Potential Risks
- Inflation risk: Rising prices can erode the purchasing power of fixed returns
- Interest rate risk: Rising rates can decrease the market value of existing notes
- Political risk: Changes in government policies or global events may affect investor confidence
Investors should carefully evaluate these risks and consider hedging strategies to protect their portfolios.
Current Trends in the 10-Year Treasury Market
As of recent years, the 10-year treasury market has experienced significant fluctuations due to changing economic conditions. The Federal Reserve's monetary policy decisions, coupled with global uncertainties, have influenced yields and investor behavior.
Recent Developments
- Lower yields amid accommodative monetary policies
- Increased demand from foreign investors seeking safe havens
- Volatility driven by geopolitical tensions and economic data
These trends underscore the dynamic nature of the 10-year treasury market and the importance of staying informed for investors.
Future Outlook for 10-Year Treasury Notes
Looking ahead, the 10-year treasury is expected to remain a vital component of global finance. As central banks navigate post-pandemic recovery and address inflationary pressures, the demand for these securities may continue to evolve.
Potential Future Scenarios
- Rising yields if economic growth accelerates
- Stable or lower yields if monetary policy remains accommodative
- Increased innovation in treasury issuance and trading mechanisms
Investors should stay attuned to economic indicators and policy announcements to anticipate future movements in the 10-year treasury market.
Conclusion
The 10-year treasury note is a cornerstone of financial stability, offering investors a secure and predictable investment option. Its significance extends beyond individual portfolios, influencing global markets and economic policy decisions. By understanding its structure, function, and risks, investors can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals.
We invite you to share your thoughts and insights in the comments below. For more in-depth analysis and updates on financial markets, explore our other articles and resources. Together, let's navigate the ever-changing world of finance with confidence and knowledge.