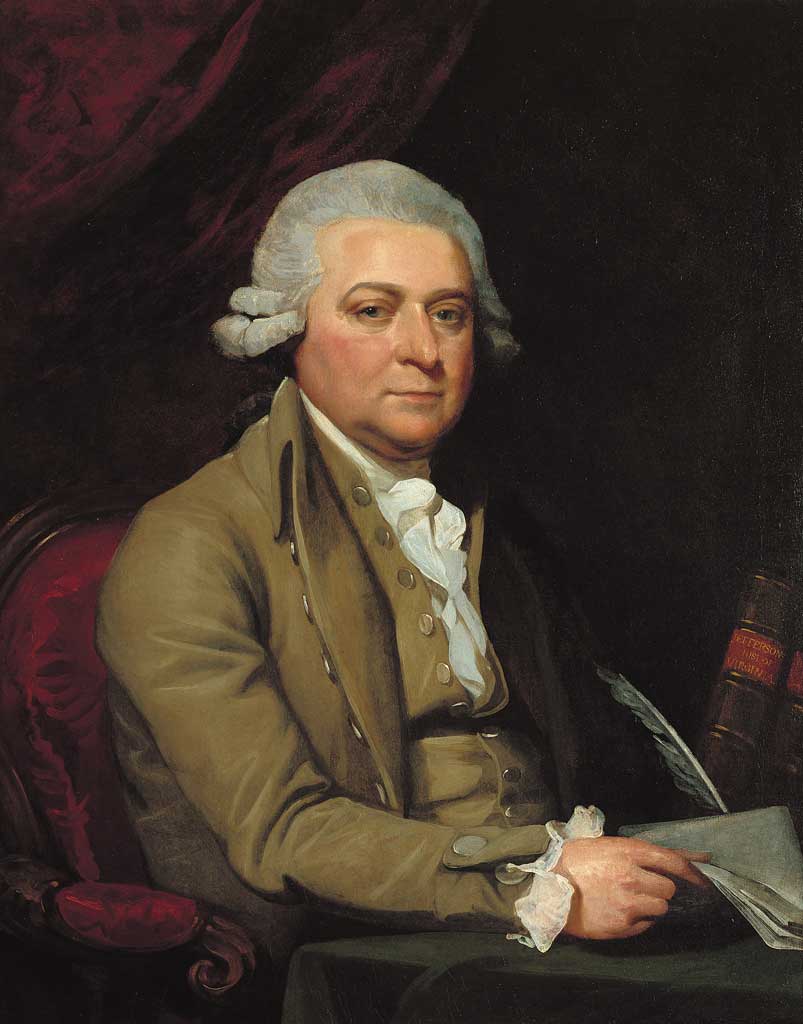
John Adams, the second President of the United States, played an indispensable role in shaping the early days of our country. His tireless work during the American Revolution, his diplomatic missions, and his presidential leadership have left a lasting mark on America's history. As one of our Founding Fathers, Adams was a key architect of the Declaration of Independence and a staunch advocate for the principles of democracy.
From his modest beginnings in Massachusetts to his rise as a prominent statesman, John Adams embodied the virtues of integrity, perseverance, and unwavering dedication to public service. His journey from a young lawyer to the presidency reflects the incredible transformation of America during the late 18th century. In this article, we'll dive deep into his life, achievements, and the enduring legacy he left behind.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the fascinating biography of John Adams, his pivotal role in the American Revolution, his time in office, and the profound impact he had on the United States. Whether you're a history buff or just curious about one of America's most influential figures, this article will give you a closer look at the life and times of John Adams.
Read also:Pamela Reed Henderson A Legendary Talent Who Keeps The Spotlight Burning
Table of Contents
- Biography of John Adams
- Early Life and Education
- Revolutionary Years and Contributions
- Diplomatic Achievements
- The Presidency of John Adams
- Key Events During His Presidency
- Family Life and Legacy
- Controversies and Challenges
- The Legacy of John Adams
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Biography of John Adams
Personal Data of John Adams
Before we dive into the incredible details of John Adams' life, let's take a quick glance at some essential facts about him in the table below:
| Full Name | John Adams |
|---|---|
| Date of Birth | October 30, 1735 |
| Place of Birth | Quincy, Massachusetts |
| Spouse | Abigail Smith Adams |
| Children | John Quincy Adams, Abigail Amelia Adams, Susanna Adams, Charles Adams, Thomas Boylston Adams |
| Occupation | Lawyer, Statesman, Diplomat, President |
| Death | July 4, 1826 |
Early Life and Education
John Adams was born on October 30, 1735, in Braintree (now Quincy), Massachusetts. His family had deep ties to New England, with ancestors who were among the region's earliest settlers. From a young age, Adams showed a sharp mind and a hunger for knowledge. He attended Harvard College, graduating in 1755, where he soaked up every bit of learning like a sponge.
After finishing his studies, Adams decided to pursue a career in law. This decision laid the groundwork for his future involvement in politics. His early days as a lawyer helped him develop strong argumentation and public speaking skills, which would serve him well in his political career. You could say he was sharpening his tools for the big stage that awaited him.
Revolutionary Years and Contributions
John Adams became a towering figure during the American Revolution. His passionate advocacy for independence and his critical role in drafting the Declaration of Independence cemented his place as one of the most influential Founding Fathers. He was a fierce opponent of British colonial policies and played a crucial role in rallying support for the revolutionary cause.
Here are some of his most significant contributions during this pivotal period:
- He was a vocal advocate for independence in the Continental Congress.
- He served on the committee tasked with drafting the Declaration of Independence.
- He provided invaluable legal expertise in defending the rights of American colonists.
Diplomatic Achievements
John Adams as a Diplomat
John Adams' diplomatic career was marked by remarkable achievements that helped strengthen the young United States. He served as a diplomat to France and the Netherlands, securing vital alliances and financial support during the Revolutionary War. These efforts were crucial in helping America gain its independence.
Read also:James Cagney A Legendary Journey Through Hollywoods Golden Age
One of his greatest accomplishments was negotiating the Treaty of Paris in 1783. This treaty officially ended the American Revolutionary War and recognized the independence of the United States. It was a monumental moment in history, and Adams played a key role in making it happen.
The Presidency of John Adams
John Adams served as the second President of the United States from 1797 to 1801. His presidency was defined by efforts to maintain peace and stability in a rapidly changing world. Despite facing numerous challenges, Adams showed incredible resilience and commitment to the principles of democracy. He wasn't just leading a nation; he was shaping its future.
Key Events During His Presidency
During his time in office, John Adams encountered several significant events that tested his leadership abilities:
- The XYZ Affair, a diplomatic scandal that almost led to war with France. Adams had to navigate these turbulent waters with care and diplomacy.
- The passage of the Alien and Sedition Acts, which sparked heated debates about civil liberties. While these laws were controversial, Adams believed they were necessary for national security.
- Efforts to strengthen the U.S. Navy and Army in response to threats from foreign powers. Adams understood the importance of a strong military in protecting the nation's sovereignty.
Family Life and Legacy
John Adams' personal life was closely intertwined with his public career. His marriage to Abigail Smith Adams was one of the most enduring partnerships in American history. Abigail was more than just his wife; she was his trusted advisor and closest confidante. Together, they raised a family that included John Quincy Adams, who would later become the sixth President of the United States. It was a legacy of leadership and service that spanned generations.
Controversies and Challenges
Despite his many accomplishments, John Adams faced criticism and controversy during his lifetime. The passage of the Alien and Sedition Acts remains one of the most debated issues of his presidency. Critics argued that these laws undermined freedom of speech and press. However, Adams firmly believed that these measures were necessary to protect the nation's security in a time of uncertainty.
The Legacy of John Adams
John Adams' legacy extends far beyond his presidency. He was a visionary leader who championed the principles of democracy, justice, and equality. His writings, including his letters and speeches, continue to inspire generations of Americans. As one of the Founding Fathers, Adams played a crucial role in shaping the nation's identity and values. His contributions to the American Revolution and his leadership during a critical period in our history have left an indelible mark on the country.
Conclusion and Call to Action
John Adams remains one of the most important figures in American history. His contributions to the American Revolution, his diplomatic achievements, and his presidency have left a legacy that continues to resonate today. By exploring his life and times, we gain a deeper understanding of the formation of the United States and the challenges faced by its early leaders.
We encourage you to learn more about John Adams and other historical figures by exploring additional articles on our website. Feel free to leave a comment or share this article with others who might find it informative. Together, we can continue to appreciate and celebrate the rich history of our nation.
Data sources: National Archives, Library of Congress, and other reputable historical institutions.